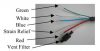
4 wire describes a sensor which has a either a wheatstone bridge strain gauge configuration or a amplified output sensor where the supply input is isolated from the signal output. 4 wire is also used to describe a resistive thermometer that is wired so that the error caused by the connecting wire on each side […]
4 Wire
Amplified Voltage Output
Amplified Voltage Output is convenient and robust measurement signal over medium distances to use with analogue to digital converters.
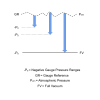
Vented Gauge
Vented Gauge (VG) is a pressure referenced to atmospheric pressure via a vent path on the reverse side of the pressure sensing diaphragm.
Pressure Units
There are many types of pressure units used depending on the country, industry and application.
IP Rating Checker
Select an IP rating from the checker and display definition for ingress protection or look up an IP rating from the table for an explanation.
IMPLR Low Range All Stainless Steel OEM Pressure Sensor
Low cost sensor for measuring small pressure ranges from 0-50 mbar (10 inH2O) to 0-1000 mbar (15 psi) of liquids or gases.
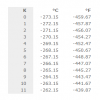
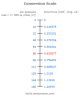
Kelvin Temperature Conversion Table for 0K to 1,000K
Look up a temperature from 0 to 1000 Kelvin (K) to convert it to degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
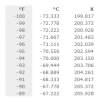
Fahrenheit Temperature Conversion Table for -100°F to 1,000°F
Look up a temperature from -100 to 1000 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) to convert it to degrees Celsius (°C) or Kelvin (K).
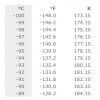
Celsius Temperature Conversion Table for -100°C to 1,000°C
Look up a temperature from -100 to 1000 degrees Celsius (°C) to convert it to degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or Kelvin (K).
MTM/N10 10mm Diameter Submersible Miniature Pressure Transducer
MTM3000 Miniature Level Sensor specially designed for inserting down very small boreholes in wells, dams and many geophysical research applications.
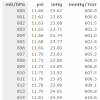
Barometric mbar/hPa, psi, inHg, mmHg/Torr Conversion Table
Look up a barometric conversion value for millibar (mbar, mb), hectopascal (hPa), pounds per square inch (psi), inches of mercury (inHg), millimetres of mercury (mmHg) or Torr pressure units.
inH2O to mmH2O, mbar, psi and mmHg Conversion Table
Look up a low pressure in inches of water column to find the conversion value in millimetres of water, millibar, pounds per square inch or millimetres of mercury.
mH2O to ftH2O, bar, psi and inHg Conversion Table
Look up a liquid level in metres of water column to find the conversion value in feet of water, bar, pounds per square inch or inches of mercury.
psi to mbar, hPa, Bar, inHg, mH2O, inH2O and ftH2O Conversion Table
Look up a pressure in pounds per square inch (psi) to find the conversion value in mb, hPa, bar, inHg, mH2O, inH2O or ftH2O.
bar to psi, inHg, mH2O and ftH2O Conversion Table
Look up a pressure for 1 to 1000 bar to find the conversion value in pounds per square inch, inches of mercury, metres of water column or feet of water column.
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the difference of two separate measurements taken at the same point, before and after a physical quantity is increased and decreased.
Deadband
Deadband is a region of pressure where a change in pressure produces no change in measurement output or control signal.
Compound Pressure Ranges
Compound pressure ranges include both a positive and negative pressure range in one pressure measurement device.
cmH2O – Centimetres of Water Column at 4 deg C Pressure Unit
Centimeters of Water Column is a manometric unit used to relate a pressure reading to the height of fresh water at a temperature of 4 degC. 1 centimeter of water gauge equals 98.0665 pascals.
bar Pressure Unit
The bar is a widely used metric unit of measurement for pressure and 1 bar equals precisely 100,000 pascals.
Absolute Pressure
A guide to absolute pressure measurement including explanations, applications and choice of products for measurements using a absolute reference.
kPa – Kilopascal Pressure Unit
The kilopascal is a x1000 multiple of the pascal unit which is the SI unit for pressure. 1 kilopascal equals 1,000 Pascals.
kg/cm² – Kilogram per Square Centimetre Pressure Unit
Kilogram Force per Square Centimeter is a pressure unit that has been largely superseded by the SI unit system of pascal units.
inHg – Inches of Mercury at 0 degrees C Pressure Unit
Inch of Mercury is a British and American unit of measure for pressure. 1 inch of mercury at 0 degrees Celsius (32 deg F) equals 3386.39 pascals. An inch of mercury at zero degrees Celsius is defined as the pressure exerted by a column of mercury with a density of 13,595.1 kg/m3 under the pull […]
inH2O – Inches of Water Column at 4 deg C Pressure Unit
Inches of water gauge or column is an english and american unit for measuring liquid level. 1 inch of water column at 4 degrees celsius equals 249.089 Pa.
Hygienic
Hygienic measurement instrumentation are designed for use by the food, drink and pharmaceutical industries, which require a high level of cleanliness in their manufacturing processes.
Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure that is generated by the weight of liquid above a measurement point, when the liquid is at rest.
HART®
HART® or Highway Addressable Remote Transducer is a type of digital communications protocol for configuring and reading instrumentation via 4-20mA signal.
hPa – Hectopascal Pressure Unit
Hectopascal is a 100x multiple of the pascal which is the SI unit for pressure.
g – Acceleration due to Gravity
Gravity (g) which is defined by an acceleration of 9.80665m/s² is the designated average accelerating force due to Earth’s gravity at sea level.
g/cm² – Grams per Square Centimetre Pressure Unit
Grams Force per Square Centimetre is a cgs system pressure unit which is now largely obsolete and officially superceded by the SI system of units.
g Effect
The g Effect is a change in performance of a pressure measuring device that is caused by a change in its orientation. Typically a pressure sensing device will have some form of flat diaphragm which will generate a change in output when flexed by a change in pressure. If a pressure sensing diaphragm is orientated […]
ftH2O – Feet of Water Column at 4 deg C Pressure Unit
Foot of Water Column is an American and English low value pressure unit
EPDM – Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer
EPDM is a type of rubber seal material which offers excellent resilience against solvents, antifreeze and aviation hydraulic fluids.
dyn/cm² – Dyne per Square Centimetre Pressure Unit
Dyne per Square Centimeter is one of the smallest pressure units and is derived from the CGS unit for force, 1 Dyne per Square Centimetre equals 0.1 pascals.
Differential Pressure
A guide to differential pressure measurement including explanations, applications and choice of products for measuring differential pressure
cmHg – Centimetres of Mercury at 0 deg C Pressure Unit
Centimeters of Mercury is a small pressure unit which represents the pressure pushing down due to gravity of any volume of liquid mercury which is 1cm high. 1 centimeter of mercury at zero degrees Celsius equals 1333.22 pascals. The use of cmHg is not as common as mmHg, it is mainly used in applications for […]
Pa – Pascal Pressure Unit
Pascal is the SI unit for pressure and is derived from other SI units using the following relationship: Pa = (kg.m/s²)/m² = kg/m.s² = N/m².
PPM – Parts Per Million
Parts Per Million (PPM) is a ratio used to describe the maximum measurement error or resolution of pressure measurement equipment.
oz/in² – Ounce per Square Inch Pressure Unit
Ounce or Ounce Force per Square Inch is a low pressure unit which is part of the British and American system of units.
LHR – Linearity, Hysteresis and Repeatability
Linearity, Hysteresis and Repeatability (LHR) is often used to describe the room temperature precision of a pressure sensor, excluding all zero & span offsets, temperature errors and long term stability. Also see non-linearity and pressure hysteresis.
N/m2 – Newton per Square Metre Pressure Unit
Newtons/Square Meter is a unit that shows how the pascal unit is derived from other SI units. Pressure is defined as Force/Area and the SI unit for Force is newtons (N) and the SI unit for Area is Sq Meters (m²). 1 newton per square metre equals 1 pascal. The N/m² pressure unit is one […]
Negative Gauge Pressure
Negative Gauge Pressure is the difference in pressure between any vacuum and atmospheric pressure. The maximum possible negative gauge pressure is always limited by the current ambient atmospheric pressure, which constantly varies, but is typically around 1 bar absolute.
mTorr – Millitorr Pressure Unit
Millitorr is a very small pressure unit used for high vacuum measurements and is a 1/1000x multiple of the torr pressure unit.
mmHg – Millimetres of Mercury at 0 deg C Pressure Unit
Millimeters of Mercury at a temperature of 0degC is a small metric pressure unit derived from the pressure generated by a 1mm tall column of mercury liquid.
mmH2O – Millimetres of Water Column at 4 deg C Pressure Unit
Millimeters of Water Column is a low range metric pressure unit derived from the hydrostatic pressure of 1mm head of water at 4 degC.
mbar – Millibar Pressure Unit
Millibar is a metric unit of pressure mainly used in European countries and is derived directly from the bar pressure unit which equals 1,000 mbar.
µHg – Micron of Mercury at 0 deg C Pressure Unit
Micron of Mercury is a very small pressure unit derived from the pressure that is generated by a 1 micrometer (1/1000mm) column of liquid mercury.
mH2O – Metres of Water Gauge at 4 deg C Pressure Unit
Meters of water gauge or column is a metric unit for measuring liquid level. 1 metre of water column at 4 degrees Celsius equals 9806.65 pascals.
MPa – Megapascal Pressure Unit
The megapascal is a x1000000 multiple of the pascal unit which is the SI unit for pressure. 1 megapascal equals 1,000,000 pascals.
tsf – Tons per Square Foot (USA, Short) Pressure Unit
Tons or Tons Force per Square Foot (USA, Short) is an American pressure unit comparable in magnitude to atmospheric pressure.
Threshold
Threshold is the amount of measurement change required before a measuring instrument reacts with a change in measurement output or produces a specified result.
at – Technical Atmosphere Pressure Unit
Technical Atmosphere is used to represent a pressure value in multiples of atmospheric pressure.
Suction Pressure
Suction pressure is a negative difference in pressure generated between two points which draws a gas or a liquid from a higher to a lower pressure state.
Static Line Pressure
Static Line Pressure is the total pressure present at a particular point along a pressurised pipe.
atm – Standard Atmosphere Pressure Unit
Standard Atmosphere is mainly used as a reference value for the average atmospheric pressure at sea level.
Specific Gravity
Specific gravity is a comparison ratio between the density of a particular substance and the density of a reference substance.
Silicon Pressure Sensors
Silicon Pressure Sensors have silicon diaphragms which have a very high elasticity and semiconductor strain gauges which produce a high span sensitivity.
Secondary Pressure Standard
Secondary Pressure Standards are pressure calibration instruments which have to be checked by primary pressure standards on a regular basis.
SG – Sealed Gauge
Sealed Gauge (SG) is a type of reference pressure measured relative to a fixed pressure of approximately 1 bar absolute.
Reference Pressure
Reference Pressure is the pressure present on the reverse or negative side of a pressure sensing element.
Primary Pressure Reference Standard
Primary pressure reference standards are used to measure and generate pressures to a high level of accuracy and repeatability for calibration purposes.
Pressure Transducers
A pressure transducer is a device which converts an applied pressure into a measurable electrical signal.
Pressure
Pressure is the amount of force applied to a unit area and is calculated by dividing the applied force by the area of the contact surface.
psi – Pounds per Square Inch Pressure Unit
Pounds or pound force per square inch (psi, lb/in², pfsi or lbf/in²) is a widely used British and American unit of measure for pressure.
psf – Pounds per Square Foot Pressure Unit
Pounds Force per Square Foot is a British (Imperial) and American pressure unit which is directly related to the psi pressure unit by a factor of 144.
Piezoresistive Strain Gauges
Piezoresistive strain gauges are a semiconductor material which changes in resistance when the material stretched or compressed.
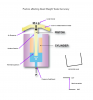
Dead Weight Tester
A Dead Weight Tester is an instrument which uses metal weights and a piston/cylinder assembly to generate pressure calibration setpoints to a high accuracy.
Torr Pressure Unit
Torr is a pressure unit which is defined as 1 standard atmosphere divided by 760 (1 atm/760 or 101325 Pa/760).
tsi – Tons per Square Inch (USA, Short) Pressure Unit
Tons or Tons Force per Square Inch (USA, Short) is one of the largest pressure units and is used in the measurement of ultra high pressures. 1 ton per square inch (usa, short) equals 13,789,500 pascals. This is the American version of tons per square inch which uses the so called short ton that is […]
tsi – Tons per Square Inch (UK, Long) Pressure Unit
Tons or Tons Force per Square Inch (UK, Long) is a very large pressure unit used historically for measuring extremely high pressures.
Zero Tare
Zero Tare is the operation of removing a zero offset to help obtain the optimal measurement over the whole measurement range.
Zero Offset
Zero Offset is the amount of deviation in output or reading from the exact value at the lowest point of the measurement range.
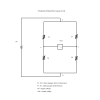
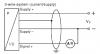
Wheatstone Bridge Strain Gauge
Wheatstone bridge strain gauge circuits are used extensively inside transducer to convert a mechanical strain into an electrical output signal.
Wet/Wet
Wet/Wet describes a differential pressure measurement device which is compatible with liquid on both the positive and negative side process connections.
Wet/Dry
Wet/Dry describes a dp measurement device for use with a liquid on the positive pressure side and a dry/non-condensing gas on the negative pressure side.
Water Density
The density of fresh water at a temperature of approximately 4 degrees Celsius is 1000 kg/m3.
Vented Cable
Vented Cable has a vent tube running through the inside of the cable to provide a vent path between the electrical connections at either end.
Turndown Ratio
Turndown Ratio describes the difference between the highest and lowest possible span of measurement output which can be set for a sensing device with a rangeable output signal such as 4 to 20mA output which is HART enabled.
Transmitter
Transmitter (Tx) is a device which converts a sensor output into an analogue signal suitable for sending over long distances without significant signal loss or interference. A common type of sensor transmitter signal is a 4 to 20 milliamp current loop output.
TEB – Total Error Band
Total Error Band (TEB) is the difference between the most negative and most positive deviation from the true measurement, determined from the combination of all known errors for a sensing device, within the constraints of the measurement and operating temperature range. Typically in the case of a pressure measurement device for example, the total error […]
TSS – Thermal Span or Sensitivity Shift
Thermal Span or Sensitivity Shift signifies the maximum amount of span that will change at any measurement point within the compensated temperature range.
Square Root Extraction
Square Root Extraction is a mathematical process which is applied to a linear measurement scale to convert it to a non-linear square root scale.
Span Sensitivity
Span Sensitivity defines the output signal characteristic of a strain gauge based sensor independent of measurement range or supply voltage.
Span
Span is the difference between the lowest and the actual reading or output signal of a measurement device.
Span Offset
Span Offset is the amount of deviation in output or reading from the exact value at a point within the measurement span.
Rangeable
Rangeable describes a measurement instrument function which allows the operator to adjust the output signal scaling to a different measurement range.
4 to 20 mA Current Loop Output Signal
4-20mA Current loop output is a type of electrical signal that is used in a series circuit to provide a robust measurement signal.
2 Wire
2 wire is used to distinguish electrical connections for measurement signals which use only two connections for carrying both the power supply and signal.
3 Wire
3 wire is used to describe a type of electrical connection for a measurement signal which has only three connections for the power supply and signal output
Wetted Parts
Wetted Parts are the measurement side components of a sensing device which are in contact with the liquid media to be measured.
UKAS Calibration Certificate
UKAS Calibration Certificate is a formal document that details the procedure and results for a calibration completed by a UKAS certified calibration laboratory.
Transducer
Transducer is a device which measures a physical quantity such as temperature or pressure and converts it into an electrical output signal.
Traceable Calibration
Traceable Calibration is carried out using equipment that is regularly calibrated by a reference source that can be traced back to a national standard.
TZS – Thermal Zero Shift
Thermal Zero Shift (TZS) is the maximum amount the output or reading at the null measurement point might deviate over the compensated temperature range
Thermal Hysteresis
Thermal Hysteresis is the measured change in output or reading at a specific measurement point taken during a sequence of increasing and decreasing temperature.
TSL – Terminal Straight Line
Terminal Straight Line (TSL) is a straight line drawn between the measurement output at zero and at full scale.
TEB – Temperature Error Band
Temperature Error Band (TEB) is the error derived from the most positive and negative deviation of all measurement points within a measurement range over the operating or compensated temperature range.
Temperature Error
Temperature Error is the deviation of a measurement reading caused by a change in media or environmental temperature.
Temperature Compensation
Temperature Compensation is a correction applied to a measurement instrument to reduce errors attributed to temperature changes in a process media which is being measured or in the surrounding environment that the instrument is being used.