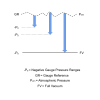
Compound pressure ranges include both a positive and negative pressure range in one pressure measurement device.
 For example you may want to purge a vessel with a vacuum pressure down to -1 bar gauge to empty it of its contents and then fill the vessel again using a pump which has a positive pressure of 5 bar gauge.
For example you may want to purge a vessel with a vacuum pressure down to -1 bar gauge to empty it of its contents and then fill the vessel again using a pump which has a positive pressure of 5 bar gauge.
If you fit 2 pressure sensors or gauges to measure the pressure, the vacuum range could be over-pressured and damaged when the +5 bar gauge is applied unless it is protected in some way. Also it is more expensive to purchase two pressure instruments.
So the solution is to the combine both pressure ranges into one pressure instrument. So in the above example if a 4 to 20mA output signal is required 4 mA would equal -1 bar gauge and 20 mA would equal +5 bar gauge.
Choose a compound range pressure sensor or gauge for measuring a process which produces both negative and positive pressures at the same position in the system.
 Compound Range Pressure Transmitters - Compound range pressure transmitters for measuring plus and minus pressures using the same device.
Compound Range Pressure Transmitters - Compound range pressure transmitters for measuring plus and minus pressures using the same device.
Help
Accuracy compromise
How does the accuracy of a compound pressure range instrument compare to the performance of individual single range devices?
The accuracy of an analogue pressure sensor is specified as a percentage of the full span which would be 6 bar in the above example. The accuracy of the lesser range, which is typically the negative one, is driven by the accuracy of the greater positive range. Since there is only one sensing diaphragm, it has to be pressure rated to the highest of the 2 pressure ranges.
A sensing diaphragm will have slightly different mechanical characteristics in either direction which are difficult to eliminate in analogue circuits.
When the sensor is relaxed there is a small degree of mechanical play, especially with more mechanised sensing technology that produces what is called a dog leg characteristic around the null point. This dog leg effect creates a zero offset in either direction which cannot be trimmed out by analogue circuitry easily.
The impact of the last two effects can be reduced if the pressure measurement instrument is digitally compensated but this is only worthwhile with sensing technology that has good long term repeatability.
Dog leg shift
What is meant by a “dog leg” shift that occurs with compound pressure ranges, is there an obvious shift in the output when transitioning from positive to negative gauge pressure?
Yes there is a shift in output across the null position of the sensing diaphragm, there is always a region of diaphragm movement around the null with very little change in output. This effect varies depending on different sensor technology, and it should always be included in the overall specification error.
Is negative part of compound range absolute or gauge
Please could you advise us for a pressure sensor with a -1 to 4 bar, which we believe has a negative rating, and therefore needs to be pressure absolute, but on the part number and data sheet says it is a gauge pressure. Could you clarify if this is correct?
Part of the range is negative, so it will also measure in the vacuum range. Absolute does not necessarily mean a vacuum range though, but refers to the type of pressure reference.
For a -1 to 4 bar pressure range, it is only possible to have a gauge reference or differential type with a negative range. It is not possible to have a negative absolute pressure because the reference is a perfect vacuum.
Alternatively the closest absolute range would be 0 to 5 bar, but this is not exactly the same unless atmospheric pressures happens to be exactly 1 bar, since a gauge reference tracks with changes in atmospheric pressure. Absolute reference is fixed to a perfect vacuum.
-1 to 4 bar compound range pressure transmitter
- SKU ID: s1-dmp331-0006
- Part No: 110-V402-1-3-100-100-1-000
- Pressure Range: -1 to 4
- Units: bar
- Range Type: Compound Gauge (-P1 to +P2)
- Output Signal: 4-20mA (2 wire)
- Accuracy: 0.35%FS >= 0.4 bar, 0.5% < 0.4bar (11-12bit resolution)
- Electrical Connection: DIN43650A plug IP65
- Process Connection: G1/2 DIN3852 male
- Process Connector Material: Stainless steel 316L
- Diaphragm Material: Stainless steel 316L
- Media Exposed Seals: FKM
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor
- Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- Measuring vacuum as an absolute range using a dp sensor
- Considerations for monitoring Landfill Water Level
- Output signal orientation for a negative gauge pressure range