Since a negative pressure range works backwards to a positive gauge or an absolute pressure range, and that zero pressure corresponds to a full scale measurement, it has led to the use of both a forward and reverse output signal to measure suction or vacuum pressure in relation to ambient atmospheric air pressure.
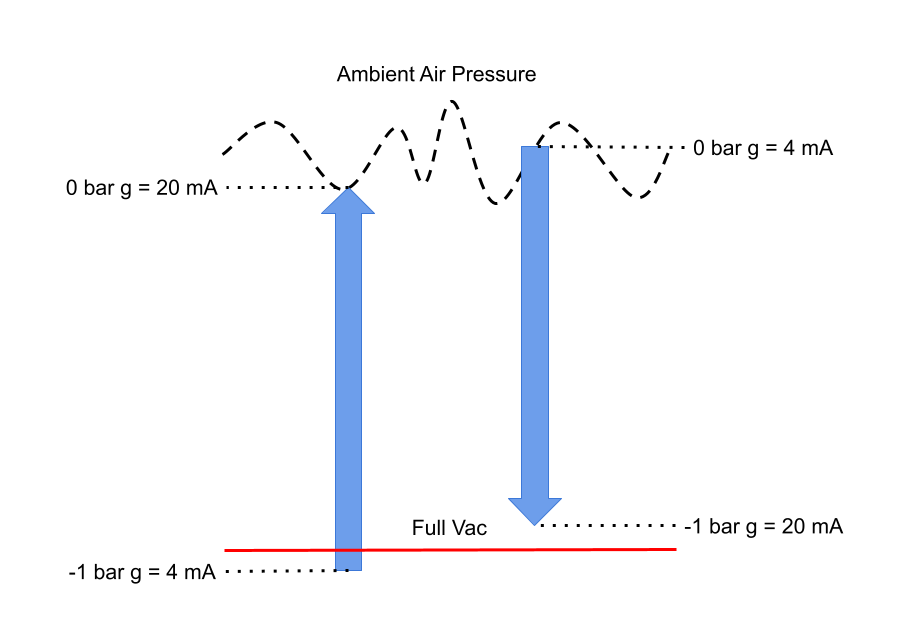
Reasons for lowest pressure to zero pressure orientation (e.g. -1 barg = 4mA, 0 barg = 20mA)
Examples of applications which have led to an output scaling starting from maximum negative gauge pressure and finishing at zero gauge pressure.
Measurement resembles an absolute range
An absolute range measures over the vacuum range to atmospheric pressure as a positive range pressure from 0 to 1 bar absolute . If a negative gauge range is configured to output 0 at -1 bar gauge and full scale at 0 bar gauge, then it will provide a measurement which closely resembles an absolute pressure range, although never exact due it having a floating reference compared to a fixed one in the case of an absolute range.
Compound range output signal must start at the lowest pressure
A compound range is a composite of two pressure ranges , a negative one and a positive one. It is only possible to start the negative range from the lowest pressure value with this type of range in order for the positive range to start at zero gauge pressure (0 barg) where the negative range finishes.
Vacuum as a positive pressure
In some application it is necessary to represent a diminishing vacuum as an increasing parameter. This could be a vessel that is being filled gas after being purged, where the direction of measurement is indicative of a rising pressure pressure, where full scale which signify that the pressure inside has equalised with the outside pressure.
Reasons for zero pressure to lowest pressure orientation (e.g. 0 barg = 4mA, -1 barg = 20mA)
Examples of applications which have led to an output scaling starting from zero gauge pressure and finishing at maximum negative gauge pressure.
Ease of zero tare at zero gauge pressure
A very easy way to improve the reading accuracy of a gauge reference pressure measurement device without a pressure calibrator is to perform a regular zero tare to take off any offset error at zero pressure. If the output of a negative range is configured to start at zero pressure, then it can be calibrated by simply allowing the pressure connection to vent to ambient air pressure.
Suction increases with negative pressure
A vacuum creates a suction pressure when compared to the surrounding ambient pressure, therefore to measure suction pressure it is necessary to read zero when there is no suction pressure and read full range at the maximum suction pressure or negative pressure.
Mimicking how a DP sensor would measure negative pressure by switching ports
A differential pressure sensing instrument can very easily be adapted to a negative gauge pressure range instrument by allowing the positive side connection to vent to the atmosphere, and connecting the negative side to vacuum. In this mode the output reading will start at zero pressure and increase as the negative pressure increases.
Mimicking how a positive gauge reference range can be used to measure negative pressure
If a positive gauge range pressure sensor is mounted so the device is surrounded by the negative pressure environment, the negative pressure will become the pressure reference and the pressure connection will be exposed to the ambient air pressure. As the negative pressure increases the sensor measurement will respond in the same way as if it was measuring a positive pressure, with a zero output when there is no negative pressure, and increase output as the pressure drops on the sensor mounted side.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range
- Measuring vacuum as an absolute range using a dp sensor
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor