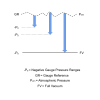
Often you will see a measurement of vacuum pressure described as an absolute pressure reading, so is there any difference between the two?
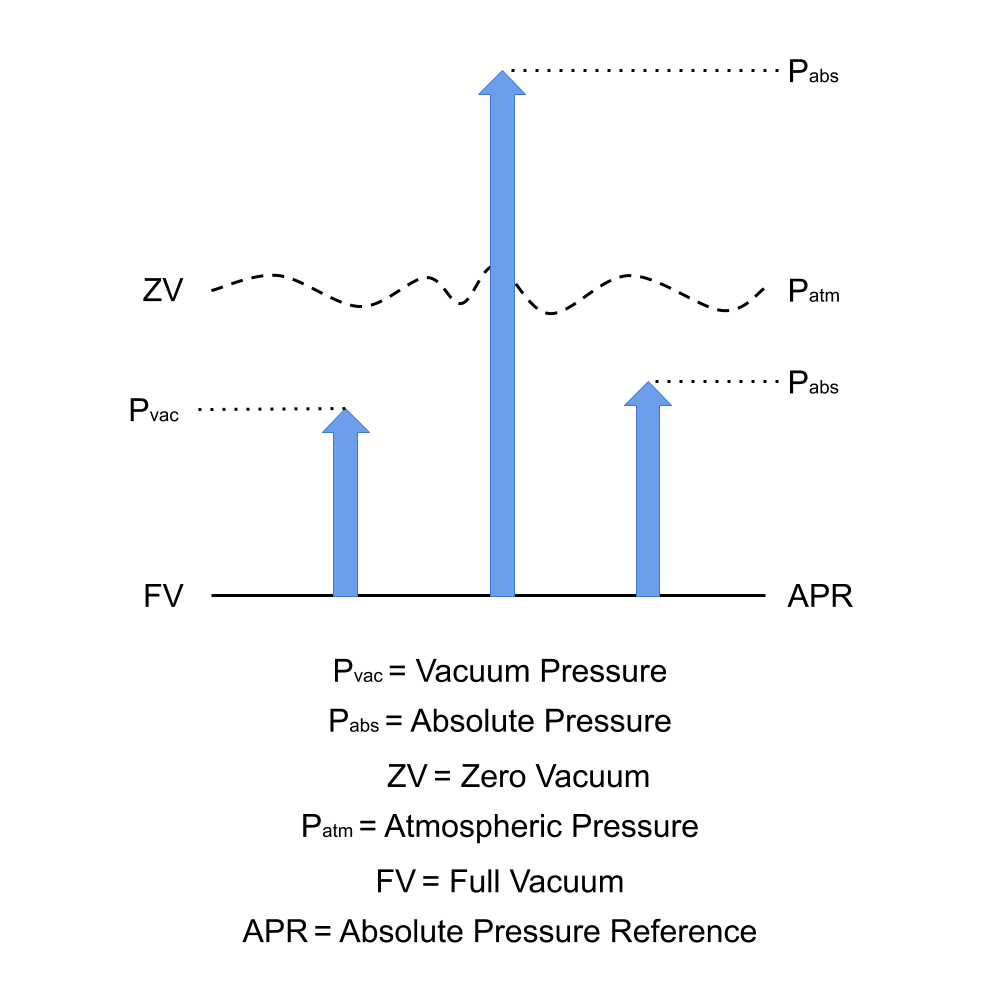
A vacuum pressure is one that is lower than the ambient environment surrounding pressure, and is typically measured relative to a perfect vacuum or full vacuum.
Since the reference pressure is not relative to another pressure and does not change, it is called the absolute reference or absolute pressure reference.
Any pressure measured relative to a full vacuum, whether above or below the surrounding ambient air pressure, is called an absolute pressure.
A vacuum pressure can always be measured and defined as an absolute pressure, but an absolute pressure can also be used to define pressures outside the vacuum range.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor
- Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range