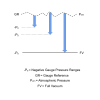
Reference Pressure is the pressure present on the reverse or negative side of a pressure sensing element.
For example the pressure reading will be zero when the total pressure measured on the positive side of the diaphragm equals the reference pressure.
Selecting reference pressure is one of the most important parameters to consider when specifying your requirements for a pressure sensing device.
It is often overlooked because the majority of pressure measurement applications have the same reference pressure and this has become the default selection if a pressure reference has not been specified.
The following sections explain what reference pressure is, why it is important and how to switch from one reference pressure type to another.
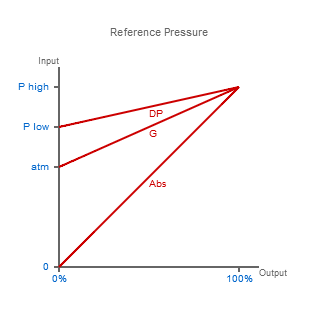
Compare Reference Pressure Types
Zero or Atmospheric Pressure?
When pressure is measured you are applying a force per unit area to a surface that is sensitive to changes in pressure. This sensing surface has two sides, one side is exposed to the measurement side, and the other side is exposed to no pressure…or is it?
“No pressure” suggests there is nothing measurable, but really it is an indication that the pressure on each side of the sensing surface is the same which results in a zero reading.
In a vast majority of applications the base pressure is atmospheric pressure, the air pressure created by the pull of earth’s gravity that surrounds everything.
If you have a pressurised vessel and you release the pressure inside to the outside air, the pressure will fall until it equalises with the external pressure. Therefore, although the sensing device would measure a zero reading, there is still a pressure present.
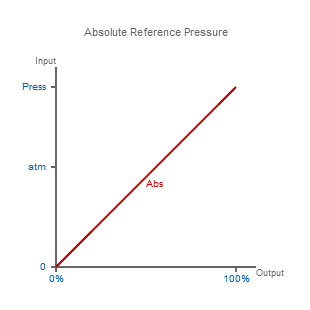
Absolute Reference Pressure
If you wanted to measure this remaining pressure you would need a device that had a sensing surface with true zero pressure on the non-measuring side. True zero pressure is a perfect vacuum, and although this is impossible to achieve, it is possible to get close enough to make adequate measurements of pressure, relative to a near perfect vacuum.
This type of measurement where the pressure on the non-measurement side is close to a perfect vacuum is called absolute pressure measurement.
Devices which measure absolute pressure are described as having an absolute reference.
An absolute reference is normally specified using “abs” or “a” as a suffix to the pressure range and pressure units (e.g. 800 – 1200 mbar a).
Examples of absolute reference pressure measurement are:
- Barometric pressure for weather monitoring
- Leak testing
- Vacuum generation
- Altitude/height measurement
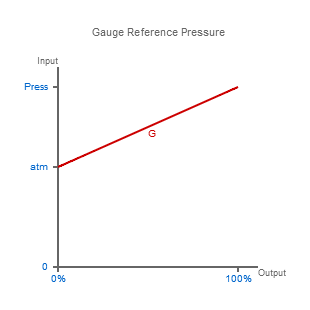
Gauge Reference Pressure
Now if you wished to ignore the remaining pressure left after venting a pressurised vessel, you would use a device where the non-measurement side is open to atmospheric pressure.
This type of measurement where the sensing surface has atmospheric pressure on one side is called gauge pressure measurement.
Devices which measure gauge pressure are described as having a gauge reference.
Gauge (g) pressure is also known as vented gauge (vg), relative (rel) or sealed gauge (sg) pressure, and is normally specified on the end of a pressure range (e.g. 10 bar g).
Examples of gauge reference pressure measurement are:
- Tyre pressure monitoring
- Hydrostatic level measurement
- Water supply pressure
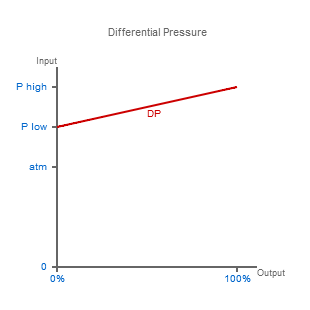
Differential Pressure Range
So what happens when the pressure on the non-measurement side of the sensing surface is something other than a perfect vacuum or atmospheric pressure?
In this type of measurement, where the pressure is unknown on both sides of the sensing surface, it is called differential pressure measurement.
Differential pressure is often described using the acronyms DP, Diff or ΔP, and they will normally be included after the pressure range and units (e.g. 30 inH2O diff).
Examples of differential pressure measurement are:
- Ventilation air flow
- Filter monitoring
- Air speed
- Hydraulic control
Changing Reference Pressure
When it comes to selecting a pressure range it is important to think about the type of pressure reference required and clearly state it in your list of specification requirements.
Neglecting to specify the pressure reference could lead to the wrong device being supplied, which could lead to significant measurement errors especially at low pressure ranges.
For example if a gauge reference device is used to measure an absolute pressure there will be an offset equivalent to atmospheric pressure with all the readings and vice versa.
Gauge ↔ Absolute Correction
Due to the different way gauge and absolute reference devices are manufactured they are not easily converted to another reference type, and therefore they will have to be returned to the manufacturer for modification or replacement. So neglecting to consider the type of reference pressure required for a pressure range could be costly to rectify.
Differential Adaptability
A differential device has one distinct advantage over gauge and absolute reference pressure devices, as a differential pressure sensing device has two ports for connecting two different sources of pressure.
Differential → Gauge Change
If you want to convert a differential device to gauge reference pressure, you simply leave the low pressure/negative side port open to atmosphere, so the pressure on the high pressure/positive side port can be measured relative to atmospheric pressure.
Differential → Absolute Change
If you want to convert a differential device to absolute reference pressure, it is a little more complicated than the switch to gauge, in that you have to find a way of creating a vacuum on the low pressure/negative side, and ensuring that it does not leak over time.
Glossary of Pressure Reference technical terms
- Gauge Reference Pressure
- MSL – Mean Sea Level
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- SG – Sealed Gauge
- Vented Cable
- Vented Gauge
Help from Pressure Reference resources
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range