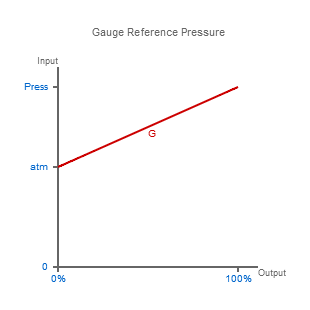
Gauge reference pressure is a pressure measured relative to atmospheric or barometric pressure.
The most used pressure reference is gauge pressure which is signified by a (g) after the pressure unit (e.g. 30 psi g), and means that the pressure measured is the total pressure minus atmospheric pressure. There are two types of gauge reference pressure which are called vented gauge (vg or g) and sealed gauge (sg).
A vented gauge pressure transmitter for example allows the outside air pressure to be exposed to the negative side of the pressure sensing diaphragm, via a vented cable or a hole on the side of the device, so that it always measures the pressure referred to ambient barometric pressure.
Thus a vented gauge reference pressure sensor should always read zero pressure when the process pressure connection is held open to the air.
A sealed gauge reference is very similar except that atmospheric pressure is sealed on the negative side of the diaphragm. This is usually adopted on high pressure ranges such as hydraulics where atmospheric pressure changes will have a negligible effect on the accuracy of the sensor so venting is not necessary.
This also allows some manufacturers to provide secondary pressure containment as an extra precaution for pressure equipment safety if the burst pressure of the primary pressure sensing diaphragm is exceeded.
There is another way of creating a sealed gauge reference and that is to seal a high vacuum on the reverse side of the sensing diaphragm. Then by adjusting the electronics the output signal is offset by 1 bar so the pressure sensor reads close to zero when measuring atmospheric pressure.
A sealed gauge reference pressure transducer will never read exactly zero because atmospheric pressure is always changing and the reference in this case is fixed at 1 bar.
Glossary of Pressure Reference technical terms
- MSL – Mean Sea Level
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- Reference Pressure
- SG – Sealed Gauge
- Vented Cable
- Vented Gauge
Help from Pressure Reference resources
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range