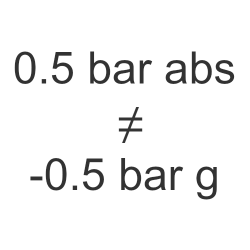 There are two reference points for measuring a vacuum pressure, you can either measure how much the pressure is below local atmospheric pressure or how much it is above absolute zero vacuum.
There are two reference points for measuring a vacuum pressure, you can either measure how much the pressure is below local atmospheric pressure or how much it is above absolute zero vacuum.
Both methods are measuring the same pressure point but each will lead to differing results over time because the measuring reference point for one is fixed (absolute zero vacuum) and the other is variable (atmospheric air pressure).
If for example you are looking to ensure that there is adequate suction pressure being drawn by a vacuum pump or you are trying to maintain a slightly lower pressure in a laboratory than the local barometric pressure to ensure no laboratory air escapes, you would be interested in measuring a negative gauge pressure. Therefore as the barometric pressure changes you will always be able to maintain suction pressure and containment of the laboratory air because the pressure you are controlling will track with changes in barometric pressure.
However, if you are looking to simulate altitude in an environmental chamber or determine whether an adequate vacuum seal has been achieved for preserving food you would measure the absolute pressure. Since you need to apply a vacuum that is a fixed value independent of the ambient baro pressure reading you can be sure that changes in atmospheric air pressure will not influence the pressure measurement.
The typical negative gauge pressure range for measuring vacuum is 0 to -1 bar gauge but if the barometric pressure is below 1 bar absolute -1 bar will never be achieved and if the barometric pressure is above 1 bar absolute then full vacuum cannot be measured. Negative gauge pressures can be combined with positive pressures to create a compound pressure range such as -1 to 2 bar gauge for processes that involve vacuum purging and pump filling.
The typical absolute pressure range for measuring vacuum pressures is 0 to 1 bar absolute.
Since negative gauge and absolute reference vacuum ranges are measuring the same pressure it is often assumed that they are the same measurement carried out in different directions. However as explained above this is not the case, so it is important to understand which type of reference is required before selecting a pressure instrument for measuring over the vacuum range .
Help
Converting negative gauge to absolute pressure
What is -0.45 bar and its conversion to a “positive” bar value?
It looks like a negative gauge value (suction/vacuum) so it can only be described as a positive value if measured as an absolute referenced value with respect to a perfect vacuum. In order to convert it to an absolute value, you will need to know the local atmospheric pressure in bar units around the same time that the pressure was measured, and then subtract 0.45 bar to work out the positive absolute pressure reading.
Negative or absolute pressure measurement for racing engine
To measure the vacuum in a racing engine, would it be better to measure absolute pressure or negative gauge pressure?
It will depend on the parameter you are measuring, typically only one way would be correct since they each have different reference points, and therefore they will each track differently as atmospheric pressure changes.
If you need to measure a parameter that is independent of atmospheric pressure, such as measuring inlet manifold air pressure with a MAP sensor, where you are determining the air density, you would use an absolute pressure sensor.
If you are monitoring boost pressure then you are interesting in measuring the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure.
Vacuum Gauge vs Vacuum Absolute
What is difference between reading pressure in vacuum gauge and vacuum absolute?
Vacuum gauge is measured from ambient air pressure in the negative direction. So for example at ambient air pressure the vacuum reading is 0 bar gauge and if a suction pressure of 0.25 bar is applied, the vacuum reading will be -0.25 bar gauge.
Vacuum absolute is measured from a perfect vacuum in the positive direction. At ambient air pressure the vacuum reading will be the barometric air pressure, let’s use 1.015 bar absolute as an example. If a suction pressure of 0.25 bar is applied the vacuum reading will be 0.765 bar absolute.
Compound vs absolute resolution of vacuum readings
I am not clear on the operation of a compound pressure transducer versus an absolute pressure transducer. Would the voltage output range on the compound transducer be split into a vacuum range and a positive pressure range providing say 0 to 2 volts signal over 29inHg to 0 vacuum, and 2 to 5 volts signal over 0 to 200 psi? Would this provide a higher resolution over the vacuum range?
A compound range will offer no accuracy benefit over an absolute range, in fact the absolute will be more accurate because there will be no “dog leg” shift effect in output as the pressure changes from positive to negative and vice versa.
A compound range is a negative and positive range combined into one instrument. The same measurement diaphragm is used to measure both the negative and positive and therefore the measurement accuracy and resolution will be dependent on the combined span of the negative and positive range.
The output contribution from each range will be proportional, so for your example above, the output will be:
- 0 to 0.33V for -29 to 0 inHg g
- 0.33-5.00V for 0 to +200 psi g
Negative absolute pressure
Is it possible to have a negative absolute pressure?
No, absolute pressure is measured with reference to a perfect vacuum so it is impossible for it to go negative. You can only measure negative pressure between two different pressures. For example if you allow atmospheric air to gradually flow into a vacuum vessel and measure pressure inside relative to outside it will show a negative pressure reading.
Absolute reading for -0.99 barg if ambient is 1.015 bara
If we say the measured pressure of ambient air is 1.015 bar absolute, and then a vacuum gauge measures a vacuum of -0.99 bar gauge, would the absolute pressure be 0.01 bar absolute?
If atmospheric pressure is 1.015 bar absolute , a vacuum of -0.99 bar gauge would be equivalent to 0.025 bar absolute.
Absolute pressure less than 0 bar and greater than 1 bar
If the atmospheric pressure is 1 bar absolute, and a pressure vacuum gauge reads less than -1 bar then does the absolute pressure still indicate 0 bar? When the pressure gauge reads more than 0 bar, then does the absolute pressure still indicate 1 bar?
You cannot have negative absolute pressure, so you are correct, but it can be more than 1 bar, there is no positive limit for absolute pressure.
If the air pressure is 1 bar absolute, you cannot have a vacuum gauge pressure less than -1 bar.
The difference between an absolute & gauge pressure measurement is always the current value of atmospheric pressure.
Absolute pressure is always referenced to a perfect vacuum so the reference is fixed, and gauge pressure is always measured relative to atmospheric pressure so the reference changes.
Strongest gauge vacuum between 110 & 500 Pa
Is 110 Pa a stronger gauge vacuum than 500 Pa?
Gauge vacuum is a negative pressure relative to atmospheric pressure, therefore 110 pascals is closer to atmospheric pressure than 500 pascals so it is a weaker vacuum.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor
- Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- Measuring vacuum as an absolute range using a dp sensor
- Output signal orientation for a negative gauge pressure range
