Find out how to use a differential pressure sensor (dp sensor) to measure a partial vacuum as a positive pressure relative to full vacuum.
- Vacuum pressure is any pressure lower than the current atmospheric pressure.
- Standard atmospheric pressure is assumed as 101325 Pa or 1 bar.
- Absolute pressure sensors have a trapped, full vacuum reference and their signal increases as the vacuum decreases (increasing pressure).
- Differential pressure sensors can be adapted for absolute pressure measurement in a vacuum by creating a vacuum reference on the negative side.
- A vacuum reference can be created using a continuous vacuum pump or by sealing a created vacuum with a leak-tight valve.
- The measured vacuum pressure is relative to the created full vacuum reference.
The vacuum range is any pressure that is lower than the current atmospheric pressure. If no atmospheric pressure is specified then an average at sea level is used, typically 1 standard atmosphere 101325 Pa, or 1 bar for convenience, since it is very close to the value of 1 atmosphere.
In the scientific world where experiments are often conducted inside evacuated vacuum chambers, the vacuum is measured using a absolute referenced pressure sensor which has full vacuum trapped on the reverse side of the sensing diaphragm. The output signal increases as the vacuum diminishes, with zero output at full vacuum, and full range output set at any pressure. Typically there is no need to set full range higher than the highest expected atmospheric pressure.
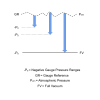
A differential pressure sensor is designed for pressure to be applied to both sides, and the mechanical design and fittings are designed to be used over a wide range of pressures including the vacuum range. It is therefore possible to apply full vacuum to the negative side of a dp sensor, to create an absolute reference, and then apply the vacuum to be measured to the positive side.
The vacuum on the negative side can be created by connecting a vacuum source from a pump to continuously maintain an absolute reference during operation, or a vacuum can be applied and then sealed off, using a suitable isolation valve able to provide a leak tight vacuum seal.
The partial vacuum pressure applied to the positive side connection of the dp sensor, will now be measured relative to full vacuum, in the same way as an absolute pressure sensor measures over the vacuum range.
Here are the steps to measure vacuum as an absolute pressure using a dp sensor:
- Choose a Suitable DP Sensor: Select a differential pressure sensor with a measurement range that covers the expected vacuum pressures you will encounter.
- Create a Vacuum Reference:
- Option 1 – Vacuum Pump: Connect a vacuum pump to the negative side of the dp sensor to continuously maintain an absolute reference.
- Option 2 – Sealed Vacuum: Apply a vacuum to the negative side of the dp sensor and then seal it with a leak-tight isolation valve.
- Connect the Vacuum Source: Apply the partial vacuum pressure you want to measure to the positive side of the dp sensor.
- Read the Sensor Output: The output of the dp sensor will represent the difference between the full vacuum on the negative side (your absolute reference) and the vacuum being measured. Since your reference is a full vacuum, the sensor’s output directly indicates the absolute pressure of the vacuum you are measuring.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- Measuring the difference in air pressure between rooms
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- What can a DP sensor be used to measure beyond differential pressure?
Related Technical Terms
- Dry/Dry
- MSL – Mean Sea Level
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- Reference Pressure
- Static Line Pressure
- Wet/Dry
- Wet/Wet
Related Online Tools
- High and Low Side Pressure to Differential Pressure Calculator
- Suction Pressure to Vacuum Calculator
- Gauge + Barometric to Absolute Pressure Calculator
- DP Flow Transmitter Output Calculator