You may not be aware but nearly every pressure measurement device you are using has a positive or negative gauge reference. It is so ubiquitous, that a gauge reference is often assumed and considered the default reference, neither mentioned in specification requirements or on manufacturers data sheets.
Although fundamentally pressure is defined and measured relative to a perfect vacuum in most scientific textbooks, it is impractical in the majority of industrial applications to measure pressure relative to an environment that does not exist naturally anywhere on terra firma. Instead most industrial equipment is located in an environment surrounded by air. To create movement of components on a machine, or to transfer a gas or fluid from one part of a process to another, a pressure has to be applied which is either greater or less than the surrounding ambient air pressure.
Local air pressure is the natural base pressure for all pressurised systems, before they are sealed and isolated from other components. This base pressure has no defined pressure value, and since local air pressure varies constantly, it is necessary to provide a way to track the gauge reference changes, to ensure a pressure reading is measured relative to the base pressure at all times.
The easiest and most practical way to continuously track a gauge reference is to provide a way to vent the reverse side of a pressure sensing device to the surrounding ambient air pressure. This will ensure that any change in the atmospheric pressure during measurement is compensated instantaneously.
Positive gauge pressure is any pressure that is measured above the current atmospheric pressure.
Negative gauge pressure is any pressure that is measured which is below the current atmospheric pressure.
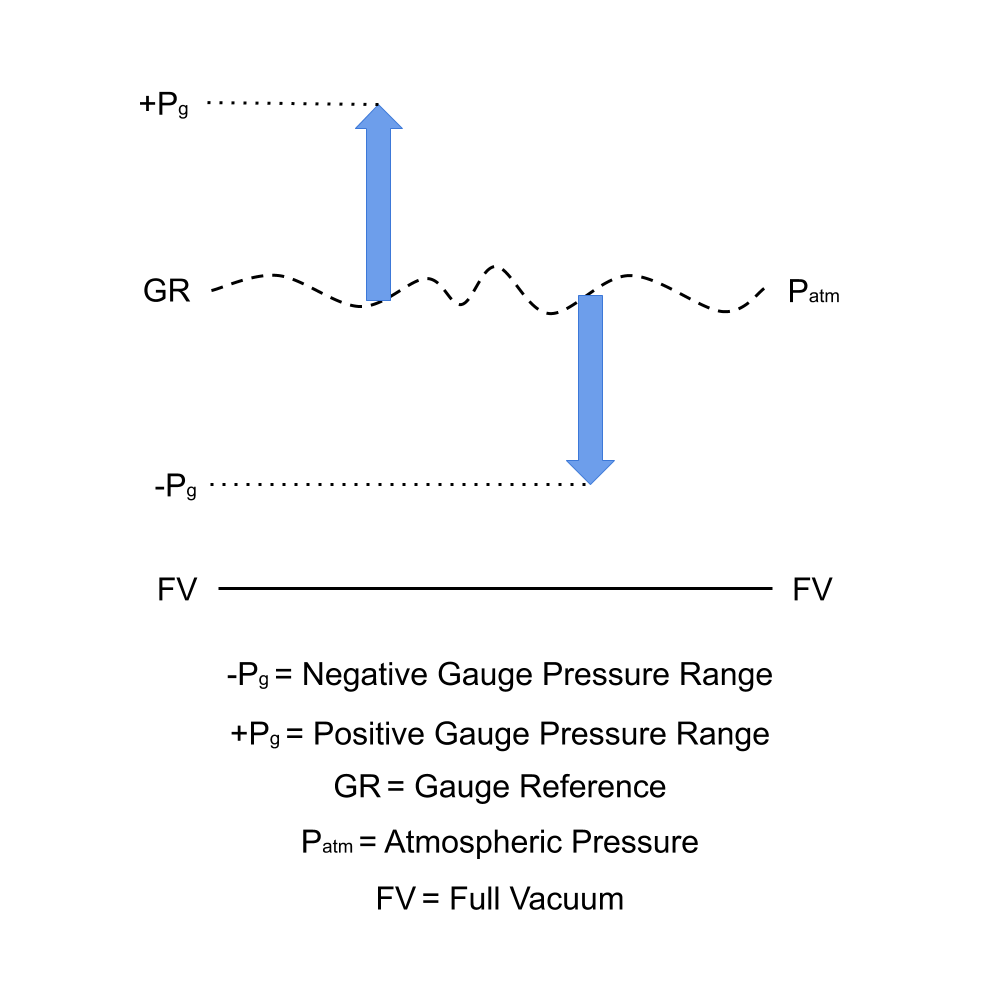
If positive or negative is not mentioned when specifying a gauge reference pressure instrument, it is safe to assume that it is a positive gauge range, since the majority of applications require a positive pressure range. A negative gauge pressure range is normally identified in requirements by the way the pressure range is described, such as minus 2 psi or negative 1 bar gauge range.
You will also see something like 10 psi vacuum ranges or vac for short, but this can lead to confusion, since a vacuum range could be defined as an absolute or a gauge reference range, both requiring different types of measurement instrument. If a g, gauge, negative or minus is mentioned as part of the vacuum range description then it is reasonable to assume it is a negative gauge range and not an absolute one.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- Measuring gauge pressure using a dp sensor
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor
- Measuring liquid level in a sealed tank with a hydrostatic pressure sensor
- What does the suffix a, abs, d, dp and diff, g, rel and sg mean after the pressure units in a pressure range?
Related Technical Terms
- Gauge Reference Pressure
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- Reference Pressure
- SG – Sealed Gauge
- Vented Cable
- Vented Gauge
