Millimeters of Mercury at a temperature of zero degrees Celsius is a small metric pressure unit which is derived from the hydrostatic pressure generated by a 1 mm tall column of mercury liquid. 1 millimeter of mercury equals 133.322… pascals.
The mmHg pressure unit is mostly used in medical industry particularly for measuring blood pressure where traditionally a liquid manometer was used as part of blood pressure testing equipment. Electronic means of measuring blood pressure are now more commonplace but the units continues to be used by the medical profession.
The pressure that is generated by a fixed height of mercury which will vary depending on the ambient temperature and local gravity, therefore it is not an absolute pressure conversion and the preferred reference values of temperature and density can vary from country to country. The conversion factors listed below are derived from mercury with a density of 13,595.1 kg/m³ and a local gravity of 9.80665 m/s².
Please use the table below to find conversion factors in other units for 1 millimetre of mercury.
To convert into mmHg from other pressure units please follow the relevant link below.
Multiple calculations can be conducted easily using our online pressure conversion tool.
See how mmHg is calculated from SI units or check the various forms of writing mmHg.
Conversion Factors
- 0.00133322 bar
- 0.0193368 psi
- 1.33322 mbar
- 133.322 N/m²
- 133.322 Pa
- 1.33322 hPa
- 0.133322 kPa
- 0.000133322 MPa
- 0.00135951 kg/cm²
- 13.5951 mmH2O 4°C (39.2°F)
- 1.35951 cmH2O 4°C (39.2°F)
- 0.0135951 mH2O 4°C (39.2°F)
- 0.535240 inH2O 4°C (39.2°F)
- 0.0446033 ftH2O 4°C (39.2°F)
- 1 mmHg 0°C (32°F)
- 0.1 cmHg 0°C (32°F)
- 0.0393701 inHg 0°C (32°F)
- 1.000000 Torr
- 1000.000 mTorr
- 0.00131579 atm
- 0.00135951 at
- 1333.22 dyn/cm²
- 0.309388 oz/in²
- 1000 µHg 0°C (32°F)
- 0.00000863249 tsi (uk, long)
- 0.00000966839 tsi (usa, short)
- 0.00139225 tsf (usa, short)
- 2.78450 psf
- 1.35951 g/cm²
Please note that the conversion factors above are accurate to 6 significant figures.
Derivation
The calculation below shows how the pressure unit millimetres of mercury (mmHg) is derived from SI Units.
Formula
- Pressure = Force / Area
- Force = Mass x Acceleration
- Mass = Density x Volume
- Volume = Area x Height
- Acceleration = Distance / (Time x Time)
SI Units
- Mass: kilogram (kg)
- Distance: metre (m)
- Time: second (s)
- Force: newton (N)
- Pressure: pascal (Pa)
Input Values
- Density = Mercury Density at 0degC = 13595.1 kg/m³
- Area = 1 m²
- Height = 1 mm = 0.001 m
- Acceleration = Standard Gravity = 9.80665 m/s²
Calculation
- 1 mmHg Mass = 13595.1 kg/m³ x 1 m² x 0.001 m = 13.5951 kg
- 1 mmHg Force = 13.5951 kg x 9.80665 m/s² = 133.3223874 N
- 1 mmHg Pressure = 133.3223874 N / 1 m² = 133.3223874 Pa
Alternate Descriptions
These are the different versions used for identifying mmHg that you may find elsewhere.
- millimetres of mercury
- millimeters of mercury
- millimetres of mercury column
- millimeters of mercury column
- mmHg
- mm Hg
Conversion Tables
Select a look up table for converting a pressure reading in millimetres of mercury column to other measurement units.
- inHg » 1 to 1,000 mmHg → 0.0393701 to 39.3701 inHg
- psi » 1 to 1,000 mmHg → 0.0193368 to 19.3368 psi
- mmH2O » 0.1 to 1,000 mmHg → 1.35951 to 13,595.1 mmH2O
- bar » 1 to 1,000 mmHg → 0.00133322 to 1.33322 bar
- Pa » 1 to 1000 mmHg → 133.322 to 133,322 Pa
- kPa » 1 to 1000 mmHg → 0.133322 to 133.322 kPa
Help
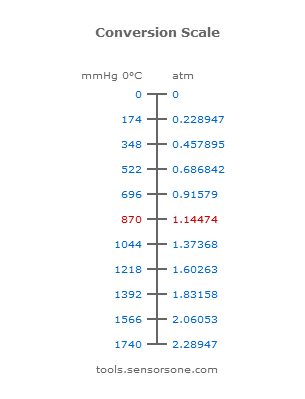
870 mmHg to atm
What is the conversion of 870 mmHg into atm units?
870 mmHg = 1.14474 atm.
Does millimetres of mercury (mmHg) = Torr
Are mmHg units really equal to Torr? I have the following information that appears to contradict this:
1 mmHg = 1.00000015001 Torr
1 Torr = 0.9999998499900226 mmHg
1 hPa = 0.750061561303 mmHg
1 hPa = 0.750061673821 Torr
There is also this:
1 Pa = 0.0075006168271 Torr
1 Pa = 0.0075006157585 mmHg
Though I think most just use these for the sake of easy math:
1 hPa = .75 mmHg
1 hPa = .02953 inHg
The value of 1 Torr is an unambiguous calculation with no variable environmental factors and is clearly defined as the 1 atm/760 or 101325Pa/760 which equals 133.322368421052631578947 pascals (calculate this on Wolfram Alpha).
So in theory every conversion should be the same albeit some variation in precision. For example our pressure converter uses a 9 digit precision and calculates 133.322387 pascals as the answer.
Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) is a little more tricky since different values are used for the density of mercury. For our conversions we use a widely accepted figure of 13,595.1 kg/m³ which is the density of mercury at 0 degrees Celsius. If you then use standard local gravity of 9.80665 m/s², the conversion from liquid column to pressure is 133.322387415 pascals.
So there is a small difference between 1 Torr and 1 mmHg, but it only shows if you are comparing conversion values of a precision of 8 significant figures or more. This level of precision is much greater than what most are looking for, so many resources show the two values as the same e.g. 133.322 pascals.
