The pressure range is the most complicated and confusing specification parameters to define for a pressure sensor. If you do not fully understand the different types of pressure that can be measured, you are likely to end up reading pressures inaccurately, or worse still, damaging the sensor before you have had a chance to correct the situation.
The two main questions that you need to ask yourself are, what is the range of pressure I need to measure over, and what baseline pressure will it be relative to?
Reference Pressure
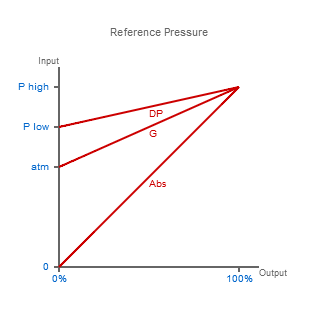
If you are measuring the direct pressure of a gas or liquid process then you will need either a gauge (g, rel) or absolute (abs, a) reference pressure range depending on whether you need to track relative to atmospheric air pressure changes (zero output = atmospheric pressure) or measure independently of atmospheric pressure changes (zero output = perfect vacuum). This will define the baseline pressure required, and will dictate the type of pressure sensor needed, since typically a pressure sensor will be manufactured to only measure gauge or absolute pressure, and cannot be modified once it has been built.
Featured gauge reference pressure sensor products
 DCT143 Compact IO-Link Pressure Sensor for OEM Mobile Hydraulics - All welded stainless steel IO-Link interface pressure sensor with a low profile for use by mobile hydraulics manufacturers to measure hydraulic pressures up to 600 bar or 9000 psi.
DCT143 Compact IO-Link Pressure Sensor for OEM Mobile Hydraulics - All welded stainless steel IO-Link interface pressure sensor with a low profile for use by mobile hydraulics manufacturers to measure hydraulic pressures up to 600 bar or 9000 psi. 400 psi g HVAC/R pressure transducer with 0.5-4.5Vdc ratiometric output - Ratiometric output pressure transducer with a 0.5 to 4.5 volt output and a measuring range of 0 to 400 psi gauge for HVAC/R (heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration) applications.
400 psi g HVAC/R pressure transducer with 0.5-4.5Vdc ratiometric output - Ratiometric output pressure transducer with a 0.5 to 4.5 volt output and a measuring range of 0 to 400 psi gauge for HVAC/R (heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration) applications.
Featured absolute reference pressure sensor products
 20 bar absolute steam pressure transducer - Pressure transducer for measuring a closed steam system pressurized by Nitrogen up to pressures of 20 bar
20 bar absolute steam pressure transducer - Pressure transducer for measuring a closed steam system pressurized by Nitrogen up to pressures of 20 bar 300°C max temperature, 0 to 300 bar, high range pressure sensor - The 35X HTC can measure up to 300 bar (and higher if necessary) on media up to temperatures of 300 degC max.
300°C max temperature, 0 to 300 bar, high range pressure sensor - The 35X HTC can measure up to 300 bar (and higher if necessary) on media up to temperatures of 300 degC max.
If you are measuring pressure between two points such as either side of an extraction fan, or across a filter, then you will need a differential pressure (dp) sensor.
Featured differential pressure sensor products
 Monitoring vacuum depression in food powder drying towers with a low range dp transmitter - DP transmitter for precise vacuum measurement and control for coconut powder drying towers to ensure consistent product quality.
Monitoring vacuum depression in food powder drying towers with a low range dp transmitter - DP transmitter for precise vacuum measurement and control for coconut powder drying towers to ensure consistent product quality. PrimAtü 10 Low Cost Low Range Differential Air Pressure Transducer - The PrimAtü 10 low cost low range differential air pressure transducer can detect and display both positive and negative differential pressure variations of very low low pressure ranges from 0.5 up to 1000 mbar/hPa, and output the pressure as a 4-20mA, 0-20mA or a 0-10Vdc analog output.
PrimAtü 10 Low Cost Low Range Differential Air Pressure Transducer - The PrimAtü 10 low cost low range differential air pressure transducer can detect and display both positive and negative differential pressure variations of very low low pressure ranges from 0.5 up to 1000 mbar/hPa, and output the pressure as a 4-20mA, 0-20mA or a 0-10Vdc analog output.
Pressure Units
Pressure ranges are typically specified by the manufacturer in bar (bar)or pounds force per square inch (psi) for medium to high pressures, and millibars (mbar), hectopascals (hPa), pascals (Pa) or inches of water column (inH2O, inWG, inWC) for low pressures. If your required pressure range is in other units then use a pressure converter to determine the pressure in common units.
Over-Range Pressure
It is important to think about the maximum pressure to be measured and the likely peak pressure that could be generated by the measured process. If there is a large difference between the two pressures then choosing a pressure sensor with a high overpressure rating to match the peak pressure is imperative to prevent calibration disturbance, mechanical damage or failure of the sensor.
Negative Pressure
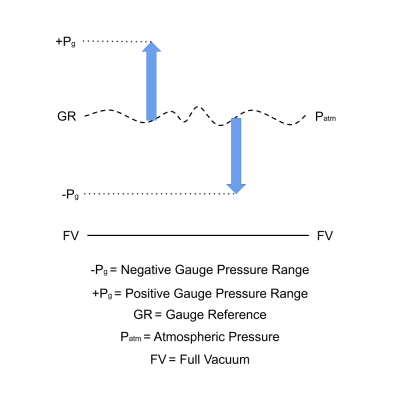 Occasionally it is necessary to measure negative pressure or pressures below the baseline reference pressure. It is only possible to do this with a gauge reference or differential pressure sensor. For example you may want to measure suction or vacuum pressure which are pressures between full vacuum and atmospheric pressure. Another example of measuring negative pressure would be to apply a reverse the differential pressure across an air filter periodically, as a preventive maintenance measure to clean the air filter and improve air flow.
Occasionally it is necessary to measure negative pressure or pressures below the baseline reference pressure. It is only possible to do this with a gauge reference or differential pressure sensor. For example you may want to measure suction or vacuum pressure which are pressures between full vacuum and atmospheric pressure. Another example of measuring negative pressure would be to apply a reverse the differential pressure across an air filter periodically, as a preventive maintenance measure to clean the air filter and improve air flow.
Compound Ranges
Negative pressure ranges can also be combined with positive pressure ranges to create a compound range or a bidirectional range. These can be used to combine vacuum and positive pressure ranges, or for measuring ventilation pressures in a duct where the air could be flowing in either direction.
Featured negative pressure sensor products
 LEO3 Current or Digital Output Pressure Gauge - LCD digital pressure gauge powered externally by a 2 wire series 4-20mA current loop or a digital interface.
LEO3 Current or Digital Output Pressure Gauge - LCD digital pressure gauge powered externally by a 2 wire series 4-20mA current loop or a digital interface. XMPi Process Plant Gauge and Absolute Pressure Transmitter - Process transmitter for measuring vacuum, steam, food, pharmaceutical, oil, gas and other pressure readings necessary for the monitoring and control of bulk production processes.
XMPi Process Plant Gauge and Absolute Pressure Transmitter - Process transmitter for measuring vacuum, steam, food, pharmaceutical, oil, gas and other pressure readings necessary for the monitoring and control of bulk production processes.
Liquid Head Pressure
It is also very common to use pressure sensors to measure liquid level by measuring the liquid head pressure. These pressure ranges are often specified in meters or feet of water column. Due to the variance in liquid density it is also possible to have specifically scaled ranges, for example 1.078 bar for a 10 metre high tank which contains a liquid of a slightly different density to water.
Featured liquid head pressure sensor products
 Submersible Hydrostatic Level Sensors & Probes - Explore submersible hydrostatic level sensors for continuous liquid level measurement. IP68 rated probes for tanks, boreholes, rivers & chemical compatibility.
Submersible Hydrostatic Level Sensors & Probes - Explore submersible hydrostatic level sensors for continuous liquid level measurement. IP68 rated probes for tanks, boreholes, rivers & chemical compatibility. Hazardous Area Submersible Hydrostatic Liquid Level Sensors - Explore our range of intrinsically safe (IS) submersible hydrostatic level sensors, designed for accurate liquid level measurement in hazardous environments
Hazardous Area Submersible Hydrostatic Liquid Level Sensors - Explore our range of intrinsically safe (IS) submersible hydrostatic level sensors, designed for accurate liquid level measurement in hazardous environments
Related Help Guides
- Determining the hydrostatic pressure range for a tank level sensor
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- Not reading zero when pressure is vented to atmosphere
- What is difference between working, burst and over pressure
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
Related Technical Terms
- Bidirectional
- Burst Pressure
- FS – Full Scale
- Gauge Reference Pressure
- MSL – Mean Sea Level
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- Reference Pressure
- SG – Sealed Gauge
- Static Line Pressure
- Vented Cable
- Vented Gauge
Related Product and Application Guides
 Low Pressure Range
Low Pressure Range Barometric Pressure
Barometric Pressure Overpressure Protection
Overpressure Protection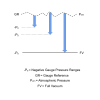 Suction Pressure
Suction Pressure Absolute Pressure
Absolute Pressure Compound Pressure Ranges
Compound Pressure Ranges Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydrostatic Pressure
Related Application Questions and Answers
Contact us about this How do you choose the correct pressure range for a pressure sensor page to request more information, or to discuss your application requirements.
