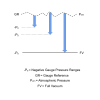
Bidirectional is typically used to indicate that a particular parameter such as an electrical signal or measurement range will generate values in both the positive and the negative direction.
For example a sensor which has a -10 mbar to + 10 mbar gauge pressure range with a 0 to 10 Vdc output is said to have a bidirectional pressure range.
Glossary of Pressure Range technical terms
- Burst Pressure
- FS – Full Scale
- Gauge Reference Pressure
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- Reference Pressure
- SG – Sealed Gauge
- Static Line Pressure
- Vented Gauge
Help from Pressure Range resources
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- What is difference between working, burst and over pressure
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range