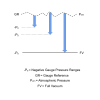
Is it possible to have a vacuum pressure measurement device with a -20 to +50 psi gauge pressure range, since I’ve never seen a pressure instrument with a range greater than -15 psi?
The majority of negative gauge vacuum range instruments are scaled to -14.5 psi or -15 psi to measure over the full vacuum range. The full vacuum range will vary because the surrounding atmospheric pressure which defines the vacuum threshold is constantly changing. However you can’t have a constantly changing negative gauge pressure range for the measurement device, so a convenient approximation of atmospheric pressure of 1 bar or 14.5 psi is used to scale and calibrate the full vacuum range of pressure measurement instruments.
Featured negative gauge pressure measurement products
 ATEX approved negative 10 mbar vacuum pressure transmitter - ATEX certified intrinsically safe pressure transmitter for measuring from 0 to minus 10 millibar gauge vacuum pressure.
ATEX approved negative 10 mbar vacuum pressure transmitter - ATEX certified intrinsically safe pressure transmitter for measuring from 0 to minus 10 millibar gauge vacuum pressure. Landfill biogas extraction well depressure pressure transmitter - Ensure efficient biogas extraction and safe operation in hazardous landfill environments with the DMP331 pressure transmitter. This intrinsically safe device accurately measures depressure in extraction wells, contributing to optimized gas collection and environmental protection.
Landfill biogas extraction well depressure pressure transmitter - Ensure efficient biogas extraction and safe operation in hazardous landfill environments with the DMP331 pressure transmitter. This intrinsically safe device accurately measures depressure in extraction wells, contributing to optimized gas collection and environmental protection.
Since pressure measurement instruments are generally not capable of measuring high vacuum to high level of accuracy, they are only used to measure over the coarse vacuum range, so rarely are the instruments relied on to measure full vacuum precisely. The reason why this is important to the discussion is because it helps explain why it is not considered necessary to set the vacuum range to a greater negative pressure such as -20 psi.
If you consider the fact that atmospheric pressure is often greater than 1000 mbar 14.5 psi, then it is sensible to conclude that a vacuum range of -14.5 psi gauge will not cover the full vacuum range. So why is the negative pressure range not greater than 14.5 psi in this case? It is probably because of a few factors, and one of those would be that the extended vacuum range would hardly ever be needed because the instrument was never intended to measure precisely at high vacuum. Another reason would be that barometric pressure at sea level, although constantly changing, stays within a fairly narrow band rarely going as high as 1050 mbar.
So that explains why we tend to only see -15 psi ranges offered by instrument manufacturers, but is it actually feasible to have a greater range of say -20 psi g?
Featured negative gauge pressure measurement products
 Leak testing set for checking 1mb/min drop at negative 10 mbar vacuum - We need a suitable gauge to use as a leak testing test set we are looking to build. We need to measure down to -10 mbar and monitor for 1 minute to ensure the leak rate is not greater than 1 mbar/minute.
Leak testing set for checking 1mb/min drop at negative 10 mbar vacuum - We need a suitable gauge to use as a leak testing test set we are looking to build. We need to measure down to -10 mbar and monitor for 1 minute to ensure the leak rate is not greater than 1 mbar/minute. Landfill biogas extraction well depressure pressure transmitter - Ensure efficient biogas extraction and safe operation in hazardous landfill environments with the DMP331 pressure transmitter. This intrinsically safe device accurately measures depressure in extraction wells, contributing to optimized gas collection and environmental protection.
Landfill biogas extraction well depressure pressure transmitter - Ensure efficient biogas extraction and safe operation in hazardous landfill environments with the DMP331 pressure transmitter. This intrinsically safe device accurately measures depressure in extraction wells, contributing to optimized gas collection and environmental protection.
In order to scale a negative gauge range sensor or instrument it is necessary to apply a known pressure in order to calibrate the device. Zero pressure is very easy to set, since you only have to vent the measurement port to ambient air pressure to check this and set the reading. However setting -20 psi will be impossible unless the atmospheric pressure happens to be 20 psi absolute or you are using a environmental test chamber that can pressurise to 20 psi absolute.
This is when you call upon the extrapolation method to determine the theoretical reading at -20 psi gauge. The simplest approach is to measure as low as possible, e.g. -14 psi and then make the assumption that it is 70% of what would be read at -20 psi. If the characteristics of the measurement device are understood, then it maybe possible to apply a non-linear correction to the calibration that would produce a better estimate of the reading at -20 psi.
So although it is probably unnecessary to have a -20 psi gauge range for the majority of negative gauge pressure range applications, it is certainly possible to manufacture and calibrate a negative 20 psi gauge range.
Featured negative gauge pressure measurement products
 Vacuum drying pressure data logger - Digital vacuum recorder for a vacuum drying pilot process.
Vacuum drying pressure data logger - Digital vacuum recorder for a vacuum drying pilot process. Dredging vacuum pressure Transmitter - Vacuum pressure sensor that will measure the vacuum pressure of a dredger suction pipe pump inlet.
Dredging vacuum pressure Transmitter - Vacuum pressure sensor that will measure the vacuum pressure of a dredger suction pipe pump inlet.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor
Related Technical Terms
Related Online Tools
Related Product and Application Guides
Related Application Questions and Answers
- Vacuum drying pressure data logger
- Low range vacuum pressure logger for 0 to -60 inH2O g
- High reading rate for measuring dynamic pressures to -200psf
- Using 25 mbar DP sensor on vacuum below 0.2 bar absolute
- Leak testing set for checking 1mb/min drop at negative 10 mbar vacuum
- Vacuum suction sensor & wall mount digital readout with switched contacts
- Vacuum pump inlet to outlet differential pressure sensor with 1500 Torr range
- Negative room pressure monitor and logger for multiple zones
- Vacuum digital gauge to measure 0 to 1000 mbar absolute
- 450 mmHg vacuum range pressure gauge
Contact us about this Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range page to request more information, or to discuss your application requirements.