Differential pressure transmitters for measuring the DP of fluids and gases across particle filters and along a length of pipe to monitor flow.
Find a pressure transmitter for measuring differential pressures with a 4-20mA current loop output signal. Measure air or liquid dp to determine flow in a pipe, negative or positive pressure between rooms or the health of a filter.
Differential pressure transmitters with a 4 to 20mA current loop output signal for measuring pressure drops of liquids or gases.
Products
 DPT100 Modbus RTU RS485 Differential Pressure Sensor - The DPT 100 is a high-accuracy differential pressure transmitter designed for fast test processes in leakage and flow measurement applications where rapid response time and high sampling rates are essential
DPT100 Modbus RTU RS485 Differential Pressure Sensor - The DPT 100 is a high-accuracy differential pressure transmitter designed for fast test processes in leakage and flow measurement applications where rapid response time and high sampling rates are essential DPS300 User Switchable Pressure Range, Volts or Current Output Low DP Sensor - The DPS 300 is a low range HVAC differential pressure sensor. The lowest possible pressure range is 0...100 pascals. 2 or 3 switchable pressure ranges, plus volts or current output are included with most standard configurations.
DPS300 User Switchable Pressure Range, Volts or Current Output Low DP Sensor - The DPS 300 is a low range HVAC differential pressure sensor. The lowest possible pressure range is 0...100 pascals. 2 or 3 switchable pressure ranges, plus volts or current output are included with most standard configurations.
 DMD331 Compact Differential Liquid Pressure Sensor
DMD331 Compact Differential Liquid Pressure Sensor DPS200 HVAC Differential Pressure Transmitter
DPS200 HVAC Differential Pressure Transmitter DPT200 Pressurised Tank Level Differential Pressure Transmitter
DPT200 Pressurised Tank Level Differential Pressure Transmitter DPT200 High One Side Overload Differential Pressure Sensor
DPT200 High One Side Overload Differential Pressure Sensor
Applications
 DP sensor for -1 to 3 bar differential water pressure and 16 bar overpressure - I am looking for a 4-20mA output DP sensor with a -1 to 3 bar differential range for use on water. The sensor will need to withstand an overpressure of 20 bar on the positive side and 1.5 bar on the negative side.
DP sensor for -1 to 3 bar differential water pressure and 16 bar overpressure - I am looking for a 4-20mA output DP sensor with a -1 to 3 bar differential range for use on water. The sensor will need to withstand an overpressure of 20 bar on the positive side and 1.5 bar on the negative side. 4 inch water column range 4-20mA differential pressure sensor for liquids - Low range wet/wet dp sensor for measuring differential pressure of a liquid from 0 to 4 inches of water column.
4 inch water column range 4-20mA differential pressure sensor for liquids - Low range wet/wet dp sensor for measuring differential pressure of a liquid from 0 to 4 inches of water column. -3 to 3 psi dp range high accuracy 4-20mA air pressure transmitter for water treatment use - A high accuracy low bi-directional range differential pressure transmitter for water treatment use to measure pressure of air over a range of -3 to 3 psi differential from two 1/4”-18 NPT internal process connections, and sending the corresponding 4-20mA signal through the 1/2" NPT internal cable gland electrical connection.
-3 to 3 psi dp range high accuracy 4-20mA air pressure transmitter for water treatment use - A high accuracy low bi-directional range differential pressure transmitter for water treatment use to measure pressure of air over a range of -3 to 3 psi differential from two 1/4”-18 NPT internal process connections, and sending the corresponding 4-20mA signal through the 1/2" NPT internal cable gland electrical connection. -200 to 200 Pa bi-directional range 4-20mA output dp pressure transmitter for venturi tube - A bidirectional low range pressure transmitter for venturi tube use to measure pressure of air in a venturi tube over a range of -200 to 200 Pa from the 6.6mm dia x 11mm barbed connections process connection, and sending the corresponding 4-20mA signal through the M12 x 1.5 cable glands with 5 internal screw terminals electrical connection.
-200 to 200 Pa bi-directional range 4-20mA output dp pressure transmitter for venturi tube - A bidirectional low range pressure transmitter for venturi tube use to measure pressure of air in a venturi tube over a range of -200 to 200 Pa from the 6.6mm dia x 11mm barbed connections process connection, and sending the corresponding 4-20mA signal through the M12 x 1.5 cable glands with 5 internal screw terminals electrical connection.
 -3 to 4 mbar dp range 4-20mA ATEX approved biogas pressure sensor for process control use on a 1bar line
-3 to 4 mbar dp range 4-20mA ATEX approved biogas pressure sensor for process control use on a 1bar line -15psig 0-10V out negative pressure transducer and display for air extraction use
-15psig 0-10V out negative pressure transducer and display for air extraction use 1 inH2O differential intrinsically safe 4-20mA out air pressure sensor for HVAC use
1 inH2O differential intrinsically safe 4-20mA out air pressure sensor for HVAC use 3inH2O differential 4-20mA nitrogen pressure sensor and display for annealing furnace flow control use
3inH2O differential 4-20mA nitrogen pressure sensor and display for annealing furnace flow control use 10bar differential range 4-20mA output air pressure sensor for leak testing use on a 110bar line
10bar differential range 4-20mA output air pressure sensor for leak testing use on a 110bar line 15psi dp range 4-20mA air pressure sensor for chamber airflow testing use on a 15psi line
15psi dp range 4-20mA air pressure sensor for chamber airflow testing use on a 15psi line Biogas HDPE cover PD blower pressure sensor
Biogas HDPE cover PD blower pressure sensor Minus 0.25 inWG differential pressure transmitter for negative air pressure difference
Minus 0.25 inWG differential pressure transmitter for negative air pressure difference
- Plenum chamber differential pressure transmitter with 100 mmWG range
- 100 mbar wet/wet 4 to 20mA differential pressure sensor and display
- 70 bar range dp transmitter with a 450 bar overpressure rating in both directions
- 2 bar water pressure difference sensor and single input process indicator
- 10 bar seawater differential pressure sensor for hazardous area
- Hydro power plant sea water high accuracy DP transmitter
- Solvent compatible +/-100mWG dp transmitter with PTFE seals
- Wet wet DP sensor for 10 inches of water range
- 150psi freshwater differential pressure sensor & panel indicator
- DP transmitter with for measuring 300inH2O gas flow across orifice plate
- Liquid compatible transmitter with 15 psi DP range and protected on either side to 300 psi
- 5 psi delta air pressure sensor with 4 to 20 mA output
Product Types
 Low Differential Pressure Transmitters - Low differential pressure transmitters for measuring small pressure differences between two measurement points on across ventilation fans, air filters or clean room walls.
Low Differential Pressure Transmitters - Low differential pressure transmitters for measuring small pressure differences between two measurement points on across ventilation fans, air filters or clean room walls.
Product Help
Liquid & Steam service installation
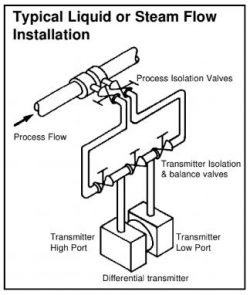 The transmitter should be installed below the process tapping points to a wall or other rigid mounting using the optional bracket assembly or similar rigid bracket. The transmitter should be piped up in compliance with the pressure transmitter installation guidelines with the process tappings taken to the side of the pipe work as illustrated in the adjacent diagram. The transmitter should be mounted within two degrees of the horizontal, small variations in mounting attitude will affect the transmitter zero point, however, this may be calibrated out during the initial commissioning procedure detailed later. When used on steam service the transmitter and impulse lines must be filled with water before system start up to prevent live steam damaging the transmitter.
The transmitter should be installed below the process tapping points to a wall or other rigid mounting using the optional bracket assembly or similar rigid bracket. The transmitter should be piped up in compliance with the pressure transmitter installation guidelines with the process tappings taken to the side of the pipe work as illustrated in the adjacent diagram. The transmitter should be mounted within two degrees of the horizontal, small variations in mounting attitude will affect the transmitter zero point, however, this may be calibrated out during the initial commissioning procedure detailed later. When used on steam service the transmitter and impulse lines must be filled with water before system start up to prevent live steam damaging the transmitter.
Gas service installation
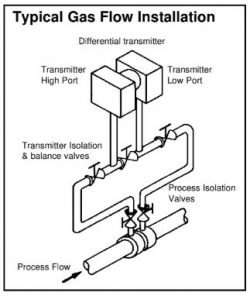 The transmitter should be installed above the process tapping points to a wall or other rigid mounting using the optional bracket assembly or similar rigid bracket. The transmitter should piped up in compliance with the pressure transmitter installation guidelines with the process tappings taken to the top of the pipe work as illustrated in the adjacent diagram. The transmitter is placed above the process measurement tapping to allow condensed liquid to drain back into the process lines. The transmitter should be mounted within two degrees of the horizontal, small variations in mounting attitude will affect the transmitter zero point, however, this may be calibrated out during the initial commissioning procedure detailed later.
The transmitter should be installed above the process tapping points to a wall or other rigid mounting using the optional bracket assembly or similar rigid bracket. The transmitter should piped up in compliance with the pressure transmitter installation guidelines with the process tappings taken to the top of the pipe work as illustrated in the adjacent diagram. The transmitter is placed above the process measurement tapping to allow condensed liquid to drain back into the process lines. The transmitter should be mounted within two degrees of the horizontal, small variations in mounting attitude will affect the transmitter zero point, however, this may be calibrated out during the initial commissioning procedure detailed later.
Specifying differential pressure transmitter requirements
Some questions to ask when defining the product requirements for a differential pressure transmitter.
Differential pressure range
What is the highest differential pressure you need to measure?
Are the high and low pressure side always the same way round, or could they switch around? If the high and low pressure side is likely to reverse back and forth, then you will need to specify a bidirectional or compound range to cover the changing direction of pressure.
Do you need to change the dp range for a different process or location? Some differential pressure transmitters allow the range to be adjusted by the user. Rangeable dp transmitters are adjusted manually by internal screws or buttons which are accessed by removing a waterproof lid or cap. Intelligent dp transmitters are adjusted via a in-built user interface, digital interface and associated software, or a special user hand terminal.
Static line pressure
What could be the highest pressure measured at either of the two process connections?
This is the general system pressure and is often significantly higher than the differential pressure measurement range. The static line pressure rating of dp transmitters will vary enormously from one type to another, so it is important to pay special attention to this parameter, since it could lead to mechanical failure if an inadequate rating is selected.
Is there a risk that full static line pressure could be applied to one side of the differential pressure transmitter? The line pressure rating does not necessarily mean that this pressure can be applied to one-side only. Most manufacturers will make it clear on their product data sheets whether the maximum static line pressure can only be applied on both sides simultaneously, or is protected from it being applied on one side only.
Overpressure
Is there a chance that the normal operating differential pressure range could be exceeded by a pressure surge or a process problem?
Maximum overpressure is the amount of differential pressure that the transmitter can withstand beyond 100% of the dp range, without pushing the performance outside of specification limits.
The overpressure rating is typically expressed as multiples of the dp range, e.g. 2x, 4x.
Bidirectional or compound differential pressure ranges, which are a combination of a positive and negative pressure range component, should have two overpressure ratings.
If the dp transmitter will only allow full static line pressure to be applied to both sides at the same time, then take care to check the negative overpressure rating is adequate. Depending on the differential sensing technology utilised, the negative overpressure rating maybe significantly lower than the positive overpressure rating.
Where a differential pressure transmitter is protected against the full static line pressure being applied to one side only, then the positive and negative overpressure rating will equal the max static line pressure rating.
Checklist for differential pressure transmitter requirements
Define your differential pressure transmitter requirements using this checklist:
- Differential pressure range?
- Static line pressure?
- Overpressure?
- Media type?
- Media temperature range?
- Environmental conditions?
- Signal output? 4-20mA
- Power supply?
- Measurement accuracy?
- Electrical connection?
- Process connection?
- Certification?
