This guide provides an overview of measuring vacuum pressure including suggested vacuum measurement products and question & answers relating to using and selecting vacuum measurement sensors & instrumentation.
Vacuum is the range of pressure which lies between zero absolute pressure (perfect vacuum) and atmospheric pressure.
 Vacuum Pressure Transmitters - Choose vacuum pressure transmitters for measurements over the low vacuum range of 25 to 760 Torr, using a absolute or negative gauge reference vacuum range.
Vacuum Pressure Transmitters - Choose vacuum pressure transmitters for measurements over the low vacuum range of 25 to 760 Torr, using a absolute or negative gauge reference vacuum range. Vacuum, Suction Pressure Data Loggers, Recorders - Select vacuum data loggers for precise recording of negative suction and absolute pressures. Ideal for process analysis, test reports, and system validation in industrial and research settings.
Vacuum, Suction Pressure Data Loggers, Recorders - Select vacuum data loggers for precise recording of negative suction and absolute pressures. Ideal for process analysis, test reports, and system validation in industrial and research settings. Vacuum Pressure Transducers - Explore vacuum pressure transducers with voltage outputs (0-5V, 0-10V, 0.5-4.5V). Select absolute or gauge references for partial/full vacuum ranges.
Vacuum Pressure Transducers - Explore vacuum pressure transducers with voltage outputs (0-5V, 0-10V, 0.5-4.5V). Select absolute or gauge references for partial/full vacuum ranges. Vacuum, Suction, Negative Pressure Gauges - Explore digital gauges using piezoresistive & capacitance sensors for low to partial vacuum, suction, and negative pressure. Ideal for industrial & lab applications.
Vacuum, Suction, Negative Pressure Gauges - Explore digital gauges using piezoresistive & capacitance sensors for low to partial vacuum, suction, and negative pressure. Ideal for industrial & lab applications. Vacuum Digital Interface Pressure Sensors - Vacuum range digital pressure sensors with serial interface offer precise pressure measurement and convenient data acquisition for vacuum applications in industrial and research environments.
Vacuum Digital Interface Pressure Sensors - Vacuum range digital pressure sensors with serial interface offer precise pressure measurement and convenient data acquisition for vacuum applications in industrial and research environments. Electronic Vacuum Switches - Electronic vacuum switches offer accurate and reliable pressure control and monitoring in vacuum systems.
Electronic Vacuum Switches - Electronic vacuum switches offer accurate and reliable pressure control and monitoring in vacuum systems. Vacuum Range Calibration Equipment - Maintain the accuracy of your vacuum sensors, gauges, and switches with high-quality vacuum calibration equipment.
Vacuum Range Calibration Equipment - Maintain the accuracy of your vacuum sensors, gauges, and switches with high-quality vacuum calibration equipment.
Vacuum pressures in the range of a few millibars up to atmospheric pressure are easily measured by diaphragm based pressure measurement instrumentation. In this range of partial vacuum pressures it is common to measure the vacuum using either a negative gauge reference or an absolute reference pressure sensing device. The choice of a negative gauge or an absolute reference will depend on whether you are interested in measuring the pressure compared to atmospheric pressure or to a perfect vacuum.
High vacuum pressures are very close to zero absolute pressure and much harder to measure with diaphragm type instrumentation. At high vacuum pressures it is necessary to use different sensor technology which is based on ionisation or thermal conductivity measurement principles.
Vacuum measurement is critical across diverse industries and research fields. Users often include design engineers developing new equipment, installation engineers setting up vacuum systems, control and instrumentation engineers integrating sensors into automated processes, and maintenance engineers ensuring continued optimal performance. These professionals work in sectors like semiconductor manufacturing, where precise vacuum control is vital for fabrication processes; aerospace, where vacuum is used in altitude simulation and component testing; and pharmaceutical production, where vacuum is essential for sterilization and drying. Research laboratories also rely heavily on vacuum technology for experiments in physics, chemistry, and materials science. Geographically, these applications span the globe, wherever advanced manufacturing, research, or specialized processes requiring vacuum are conducted.
Questions & Answers
0 bar absolute = -1 bar gauge
Is zero bar absolute the same as minus 1 bar gauge?
No, only when atmospheric pressure happens to correspond exactly to 1 bar absolute which rarely happens.
Does 1 bar cover the vacuum range
Is a minus 1 bar range adequate for measuring over the vacuum range?
For most applications yes, especially if measuring low suction pressures. If measuring a very high vacuum to some degree of accuracy, it is best to measure with a positive absolute range, since a negative gauge device will give different readings due to the changes in atmospheric pressure.
Technology used to measure over vacuum range
What type of sensing technology is used for measuring in the vacuum range?
For vacuum ranges 0-100 mbar up to 0-1000 mbar absolute it is usual to use a lower cost strain gauge diaphragm type. For ranges from 0-1 mbar up to 0-1000 mbar absolute, capacitive or inductive sensing techniques are the typical methods for measuring higher vacuums more precisely and with less drift. For ultra high vacuum ranges below 0-1 mbar it is not possible to measure this low a pressure with electromechanical devices and it is necessary to use less direct methods such as thermal conductivity and ionisation techniques.
Vacuum units
What pressure units are used for measuring vacuum pressures?
Vacuum level variations in a pumped chamber
Will the vacuum level be the same at the opposite end to the suction end of a chamber where a vacuum pump is connected?
If there is flow of gas, then you should expect there to be some difference in pressure, but it will depend on flow rate, size of volume and any restrictions between pump and end of chamber. If the suction pressure is static with no flow, then the vacuum pressure will equalise it all points.
Vacuum Gauge vs Vacuum Absolute
What is difference between reading pressure in vacuum gauge and vacuum absolute?
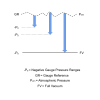
Vacuum gauge is measured from ambient air pressure in the negative direction. So for example at ambient air pressure the vacuum reading is 0 bar gauge and if a suction pressure of 0.25 bar is applied, the vacuum reading will be -0.25 bar gauge.
Vacuum absolute is measured from a perfect vacuum in the positive direction. At ambient air pressure the vacuum reading will be the barometric air pressure, let’s use 1.015 bar absolute as an example. If a suction pressure of 0.25 bar is applied the vacuum reading will be 0.765 bar absolute.
Related Help Guides
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range
- Measuring vacuum as a negative gauge pressure using a dp sensor
- Can you measure vacuum using a gauge pressure range
- Can you have a minus 20 psi gauge vacuum measurement range
- Measuring vacuum as an absolute range using a dp sensor
- Output signal orientation for a negative gauge pressure range
Related Technical Terms
Related Online Tools
Related Product and Application Guides
Related Application Questions and Answers
- Vacuum drying pressure data logger
- Low range vacuum pressure logger for 0 to -60 inH2O g
- High reading rate for measuring dynamic pressures to -200psf
- Using 25 mbar DP sensor on vacuum below 0.2 bar absolute
- Leak testing set for checking 1mb/min drop at negative 10 mbar vacuum
- Vacuum suction sensor & wall mount digital readout with switched contacts
- Vacuum pump inlet to outlet differential pressure sensor with 1500 Torr range
- Negative room pressure monitor and logger for multiple zones
- Vacuum digital gauge to measure 0 to 1000 mbar absolute
- 450 mmHg vacuum range pressure gauge
Contact us about this Vacuum page to request more information, or to discuss your application requirements.