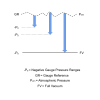
Static Line Pressure is the total pressure present at a particular point along a pressurised pipe.
It is often quoted on the specifications for differential pressure sensors as an indicator of the maximum pressure that can be applied to both the high and the low side pressure ports at the same time. This should not be confused with the over-pressure limit which is related to the differential pressure range rather than the static line pressure.
Featured differential pressure measurement products
 DPT200 Pressurised Tank Level Differential Pressure Transmitter - Pressurised tank liquid level differential pressure cell transmitter for process plant storage.
DPT200 Pressurised Tank Level Differential Pressure Transmitter - Pressurised tank liquid level differential pressure cell transmitter for process plant storage. Monitoring AHU cooling coil efficiency with a DP transmitter - Low-range differential pressure transmitter for integration with a USB data acquisition module to monitor the efficiency of AHU cooling coils, enabling a predictive maintenance schedule based on real-time data.
Monitoring AHU cooling coil efficiency with a DP transmitter - Low-range differential pressure transmitter for integration with a USB data acquisition module to monitor the efficiency of AHU cooling coils, enabling a predictive maintenance schedule based on real-time data.
Glossary of Pressure Range technical terms
- Bidirectional
- Burst Pressure
- FS – Full Scale
- Gauge Reference Pressure
- Negative Gauge Pressure
- Reference Pressure
- SG – Sealed Gauge
- Vented Gauge
Help from Pressure Range resources
- Determining the hydrostatic pressure range for a tank level sensor
- Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
- What is the difference between gauge and absolute pressure measurement
- What is difference between working, burst and over pressure
- What is the difference between vacuum and absolute pressure
- What does negative and positive gauge pressure mean
- Measuring negative pressure using a positive differential pressure range