| Calculate Hydraulic Cylinders Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Select Answer Mode |
|
| Set Units Shortcut | |
Click save settings to reload page with unique web page address for bookmarking and sharing the current tool settings
Change the answer mode for this tool by selecting piston force, bore diameter, linear displacement, pressure or displaced volume as the parameter to calculate instead
Related Tools
- Push Pull hydraulic cylinder pressure, diameter and force calculator
- Piston cylinder pressure and diameter to force calculator
- Piston cylinder force & diameter to pressure calculator
- Piston cylinder force & pressure to diameter calculator
User Guide
This tool will calculate force, diameter and displacement parameters for two hydraulic piston cylinders of different diameters connected together.
Two connected hydraulic piston cylinders are a common way of demonstrating how hydraulics can multiply a force and transmit it through a liquid medium by simply using a larger bore diameter for the cylinder transmitting the force.
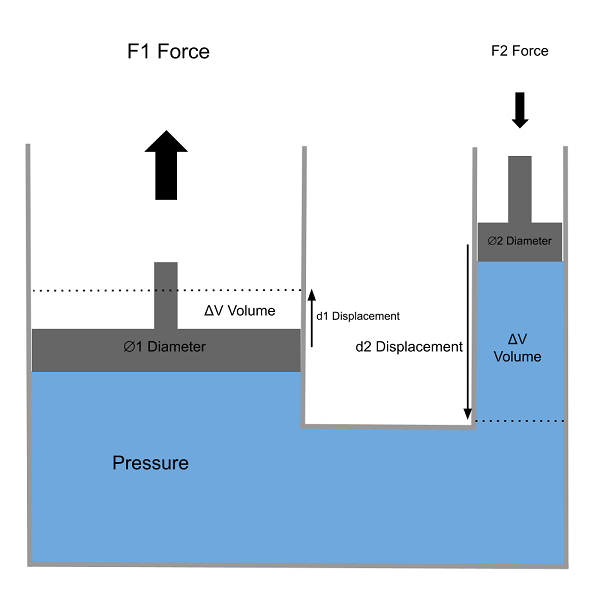
In a balanced system where the force applied to each piston does not cause any displacement, the pressure generated in the fluid connecting the two cylinders, by a force acting on one of the pistons, will be transmitted to the other cylinder by an equivalent amount. Since pressure equals force divided by area, the resulting force on the other piston is proportional to the ratio of cylinder areas.
If the hydraulic fluid connecting the two cylinders is assumed to be non-compressible, any volume displaced in cylinder 1 due to piston movement, will result in an equal amount of volume displaced in cylinder 2. Since each cylinder has a different diameter, the linear movement of each piston will be different. The smaller diameter piston will move further than the larger diameter piston, in order to displace the same volume.
Formulas
The formulas used by this two connected hydraulic cylinders calculator to determine each individual parameter are as follows:
P = F1 / A1 = F2 / A2
ΔV = A1 · d1 = A2 · d2
A1 = π · ø12 / 4
A2 = π · ø22 / 4
ø1 = 2 · √ (A1 / π)
ø2 = 2 · √ (A2 / π)
F1 = F2 · ø12 / ø22
ø1 = √(ø22 · F1 / F2)
ø1 = √(ø22 · d2 / d1)
d1 = ø22 · d2 / ø12
F2 = F1 · ø22 / ø12
ø2 = √(ø12 · F2 / F1)
ø2 = √(ø12 · d1 / d2)
d2 = d1 · ø12 / ø22
P = 4 · F1 / (π · ø12)
P = 4 · F2 / (π · ø22)
ΔV = π · ø12 · d1 / 4
ΔV = π · ø22 · d2 / 4
Symbols
- A1 = Effective area of cylinder 1
- A2 = Effective area of cylinder 2
- ø1 = Bore diameter of cylinder 1
- ø2 = Bore diameter of cylinder 2
- F1 = Force on cylinder 1 piston
- F2 = Force on cylinder 2 piston
- d1 = Linear displacement of cylinder 1 piston
- d2 = Linear displacement of cylinder 2 piston
- P = Pressure in connected cylinders
- ΔV = Displaced volume from piston movement in each cylinder
- π = Pi = 3.14159…
F1 – Force
This is the force acting on the piston in cylinder 1 when the system is balanced without any displacement of the piston.
ø1 – Diameter
This is the bore diameter of cylinder 1 or the piston diameter in cylinder 1. It is assumed that there is no gap between the piston and cylinder. If the effective diameter is known, which takes into account the clearance between the piston and cylinder, then this should be used instead.
d1 – Displacement
This is the linear displacement of the piston in cylinder 1. Displacement of the pistons is caused by pushing one of the pistons down, which results in the other piston being pushed up by a lesser or greater degree depending on the difference in diameter.
F2 – Force
This is the force acting on the piston in cylinder 2 when the system is balanced without any displacement of the piston.
ø2 – Diameter
This is the bore diameter of cylinder 2 or the piston diameter in cylinder 2. It is assumed that there is no gap between the piston and cylinder. If the effective diameter is known, which takes into account the clearance between the piston and cylinder, then this should be used instead.
d2 – Displacement
This is the linear displacement of the piston in cylinder 2. Displacement of the pistons is caused by pushing one of the pistons down, which results in the other piston being pushed up by a lesser or greater degree depending on the difference in diameter.
Pressure (P)
This is the pressure of the fluid in a balanced state, when the forces applied to each piston do not cause movement or any volume to be displaced.
Volume Displaced (ΔV)
This is the volume displaced in each cylinder due to movement of the pistons.
