 Voltage signal out pressure transducers protected to IP 68 ingress protection rating for immersing in water or other compatible liquids.
Voltage signal out pressure transducers protected to IP 68 ingress protection rating for immersing in water or other compatible liquids.
These pressure transducers have highly waterproof electrical interfaces for permanent installation underwater. IP68 pressure transducers are used to measure liquid level and pressures in storage tanks, ponds, rivers and boreholes.
Watertight volts out transducers for submerging to measure liquid depth/level or underwater system pressures. These transducers can be submerged underwater as part of a permanent installation such as in a borehole or a liquid storage tank.
No installation mounting is required for these submersible transducers, each is fitted with a cable designed to support the weight of the transducer and cable, although it is recommend to lower inside a stilling well where the liquid is moving such as in tidal water or groundwater pumping installations.
Submersible pressure transducers are typically vented to compensate for ambient pressure changes when measuring liquid depth, but non-vented versions are also available for applications where the cable is not brought to the surface.
Products
 SSPT Subsea Wet-Mateable Electrical Connector Pressure Sensor - This stainless steel ceramic sensing diaphragm based subsea connector pressure sensor provides a unamplified ratiometric millivolt output or an amplified analogue output signal corresponding to ranges from 0…1 bar (14.50 psi) up to 400 bar ( 5800 psi).
SSPT Subsea Wet-Mateable Electrical Connector Pressure Sensor - This stainless steel ceramic sensing diaphragm based subsea connector pressure sensor provides a unamplified ratiometric millivolt output or an amplified analogue output signal corresponding to ranges from 0…1 bar (14.50 psi) up to 400 bar ( 5800 psi).
Applications
 300 foot sea depth waterproof pressure sensor with 0-5V signal - Waterproof submersible pressure sensor for lowering to ~300 feet below sea level.
300 foot sea depth waterproof pressure sensor with 0-5V signal - Waterproof submersible pressure sensor for lowering to ~300 feet below sea level. 10 kPa g range 0-5Vdc output submersible freshwater pressure sensor for water treatment use - A gauge pressure sensor for water treatment use to measure pressure of freshwater over a range of 0 to 10 kPa g from the G1/4 male process connection, and sending the corresponding 0-5Vdc signal through the submersible electrical connection.
10 kPa g range 0-5Vdc output submersible freshwater pressure sensor for water treatment use - A gauge pressure sensor for water treatment use to measure pressure of freshwater over a range of 0 to 10 kPa g from the G1/4 male process connection, and sending the corresponding 0-5Vdc signal through the submersible electrical connection.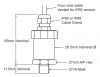 Irrigation water pressure transducer for pressures up to 60 bar - Voltage output pressure transducer with a 0 - 5V dc signal out for measuring irrigation piping water pressure form 0-60bar.
Irrigation water pressure transducer for pressures up to 60 bar - Voltage output pressure transducer with a 0 - 5V dc signal out for measuring irrigation piping water pressure form 0-60bar.
